Financial markets don’t always move smoothly. Every once in a while, the price shifts rapidly, leaving behind gaps where little to no trading takes place. These price inefficiencies, known as Fair Value Gaps, are key areas where the market may return to fill unfilled orders. The term FVG was coined by Inner Circle Trader (ICT) and is one of the most powerful concepts in trading. It has been the core of my personal trading strategy over the last few years.
ICT Fair Value Gaps are a pattern, but they’re different from classical chart patterns like the flag pattern. They are widely used in smart money trading (ICT Trading) to identify high-probability setups in Forex, stocks, crypto, and even binary options. For binary options trading specifically, FVGs can be used as precise entry points for short-term trades.
• Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are price inefficiencies formed when the market moves aggressively in one direction, creating gaps between three consecutive candles.
• FVGs can act as support and resistance zones, providing high-probability trade entries when price reacts to them.
• For binary options trading, FVGs can serve as precise entry points, with trades executed upon price rejection from the gap.
• Common mistakes when trading FVGs include misidentifying weak gaps, ignoring higher timeframes, and using overly tight stop losses.
• To maximize accuracy, traders should confirm FVG setups with liquidity hunts, displacement moves, and alignment with the overall market structure.
What Is a Fair Value Gap in Trading?
An FVG in trading is a price imbalance that occurs between three consecutive candles. It shapes when the market moves aggressively in one direction. The FVG will be the part of the middle candle’s body between the first and third candle’s wicks. So, let’s get this out of the way quickly: if the mentioned wicks cover all of the middle candle’s body, there will be no ICT fair value gap.
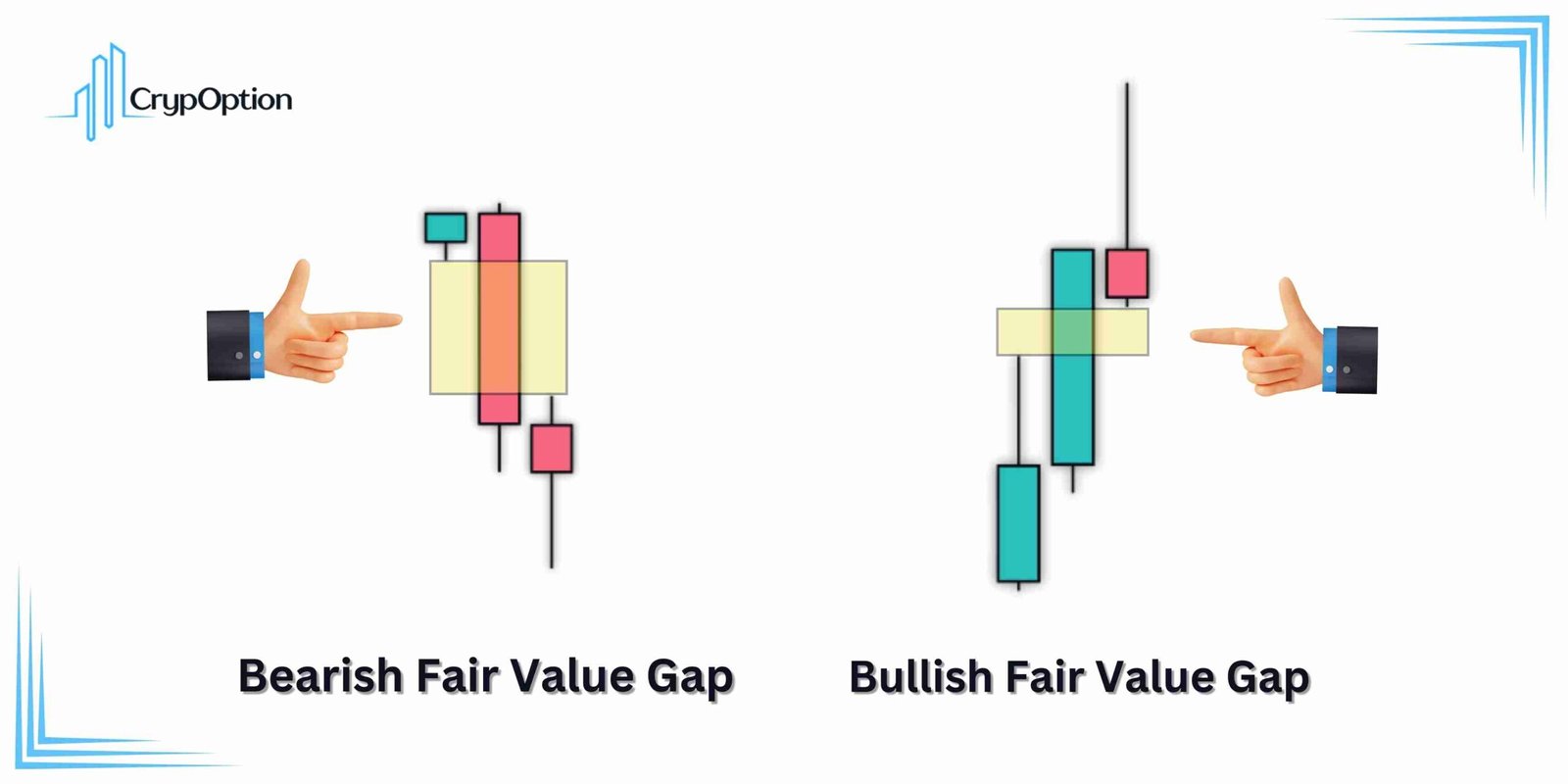
The image above shows a schematic of both bearish and bullish fair value gaps. According to ICT trading concepts, the FVG is a zone where liquidity might still be resting. Institutional and smart money traders often look at these gaps as areas where the price may return and pick up more orders before continuing in its original direction.
The fair value gap is a core concept in many strategies, including the ICT Silver Bullet, which is one of the most straightforward trading strategies you can get from ICT concepts.
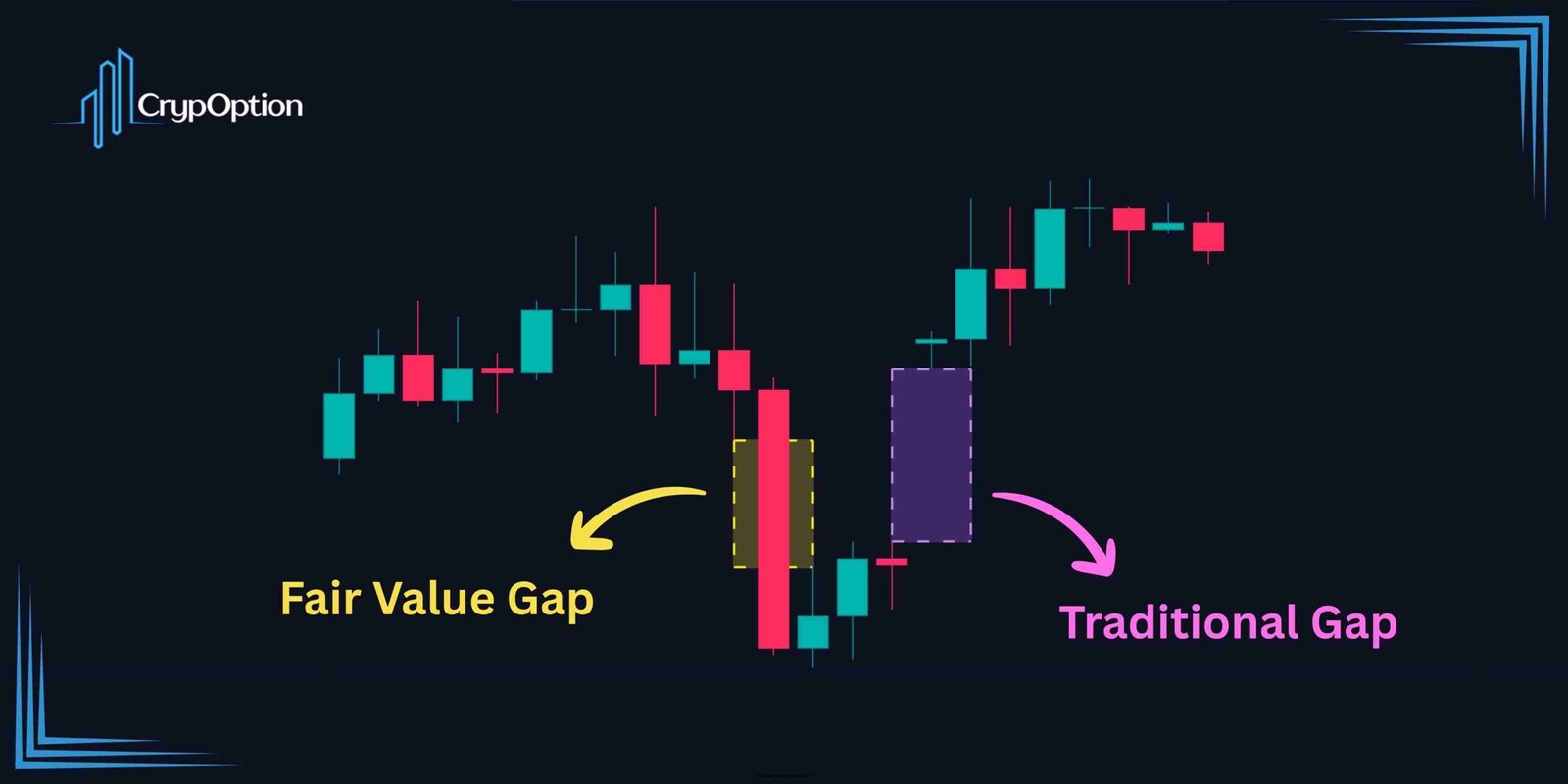
Fair Value Gap vs Traditional Gaps
Traditional trading gaps are usually formed between market sessions (like in stocks) or during high-momentum moves where the market jumps over a certain price range as no trading occurs there. So, traditional gaps are visible as voids on the chart.
On the other hand, FVGs appear within active price action and on any timeframe. In fact, for one to form, it is essential to have a candle with a body, and trading should be done in the specific range, although the price quickly moves away again.
How to Identify FVGs in Trading
Identifying fair value gaps is quite easy once you understand their structure. They typically appear during a strong, impulsive move. When the price moves aggressively in one direction in a short period of time, it leaves a gap between the high or low of the first and third candles. As already mentioned, the part of the middle candle’s body that is not traded through by the wick of the first and third candles will be our FVG.
In order to identify fair value gaps, just follow the two steps below. After a while, you will get the hang of it and can recognize all of them in a quick look.
- Look for Relatively Impulsive Moves: Valid FVGs form when price moves rapidly and leaves a visible gap behind. Pro tip: These moves often occur after liquidity hunts.
- Identify the Gap Between the First and Third Candle: If there’s an untapped part on the second candle’s body between the wick of the first and third candle, it will be the FVG we’re looking for.
Bullish vs. Bearish FVGs
While the concept is the same, the use case of bullish and bearish fair value gaps are the opposite. Therefore, make sure to identify them correctly.
- Bullish FVGs usually form when the price surges upward. A bullish fair value gap is where the middle candle is bullish.
- Bearish FVGs also often form when the price drops sharply. However, the bearish fair value gap forms when the middle candle of our pattern is bearish.
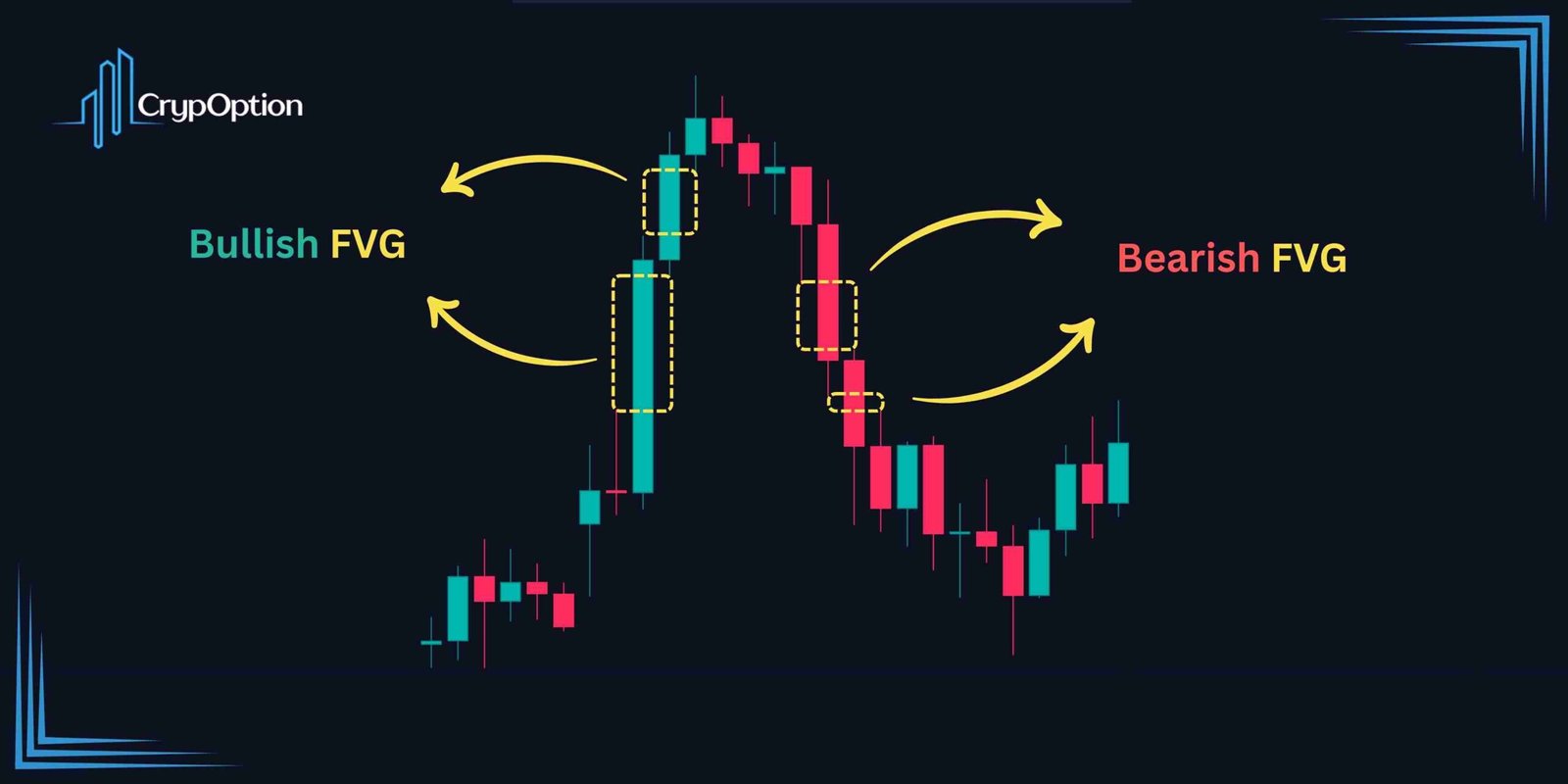
Both bullish and bearish fair value gap examples are visible on the chart above. As you can see, they occur when the price move is significant relative to the recent price action.
How to Trade Fair Value Gaps
Well, Fair Value Gaps can both attract and reject the price. What I mean is that the price sometimes aims to fill unfilled ones. This is because they are essentially imbalances, and the market tends to fill imbalances over time. So, you can use it as a target for your trades. Here is a target Fair Value Gap example:
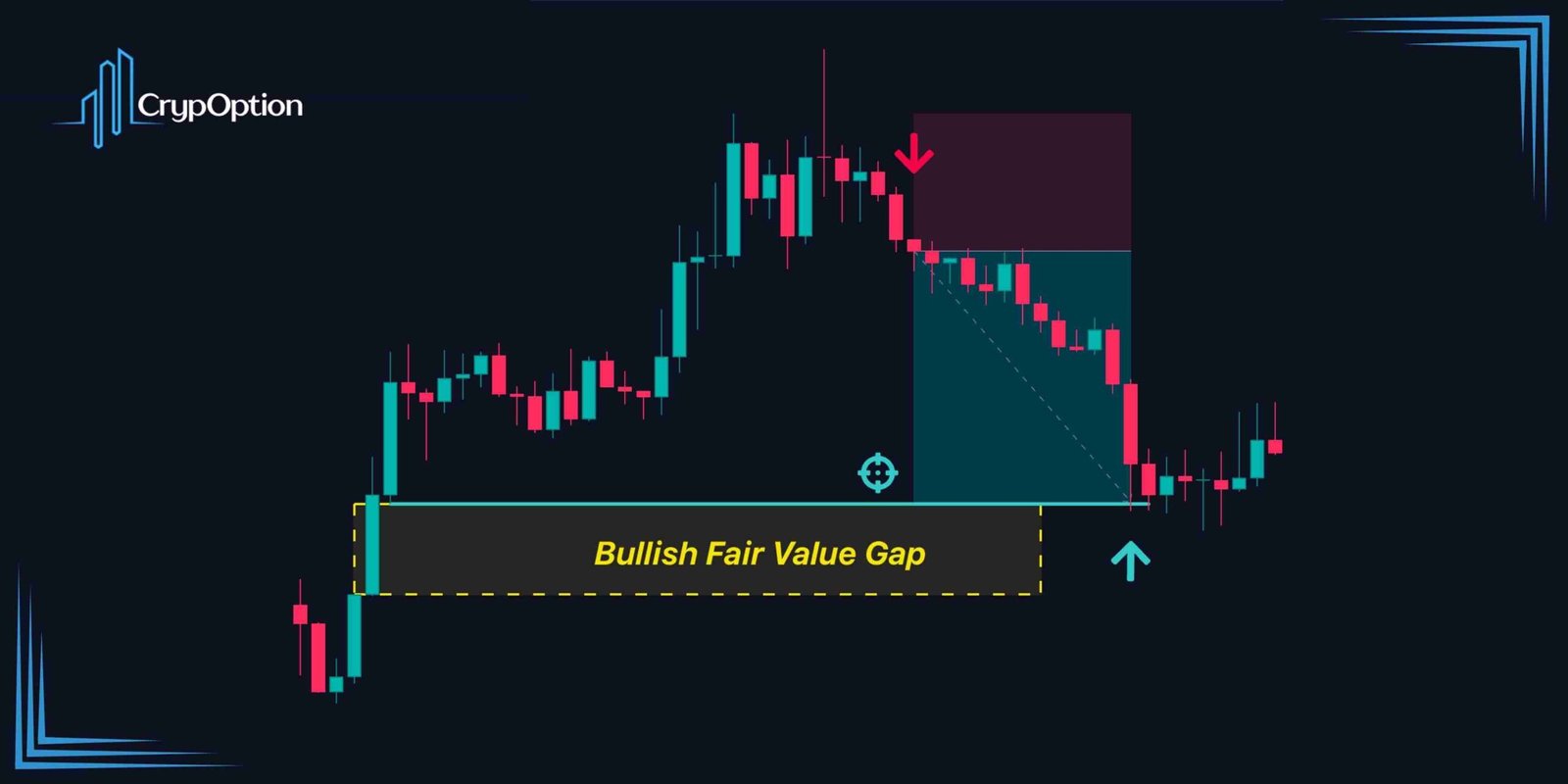
On the other hand, Fair Value Gaps can work as support and resistance levels. Unfilled FVGs can attract the price, and once they are filled (even partially), they can act as an obstacle and overturn the price action. So, a bullish Fair Value Gap can act as a support level, while a bearish fair value gap can be a resistance zone. As a result, you can also use them for trade entries.
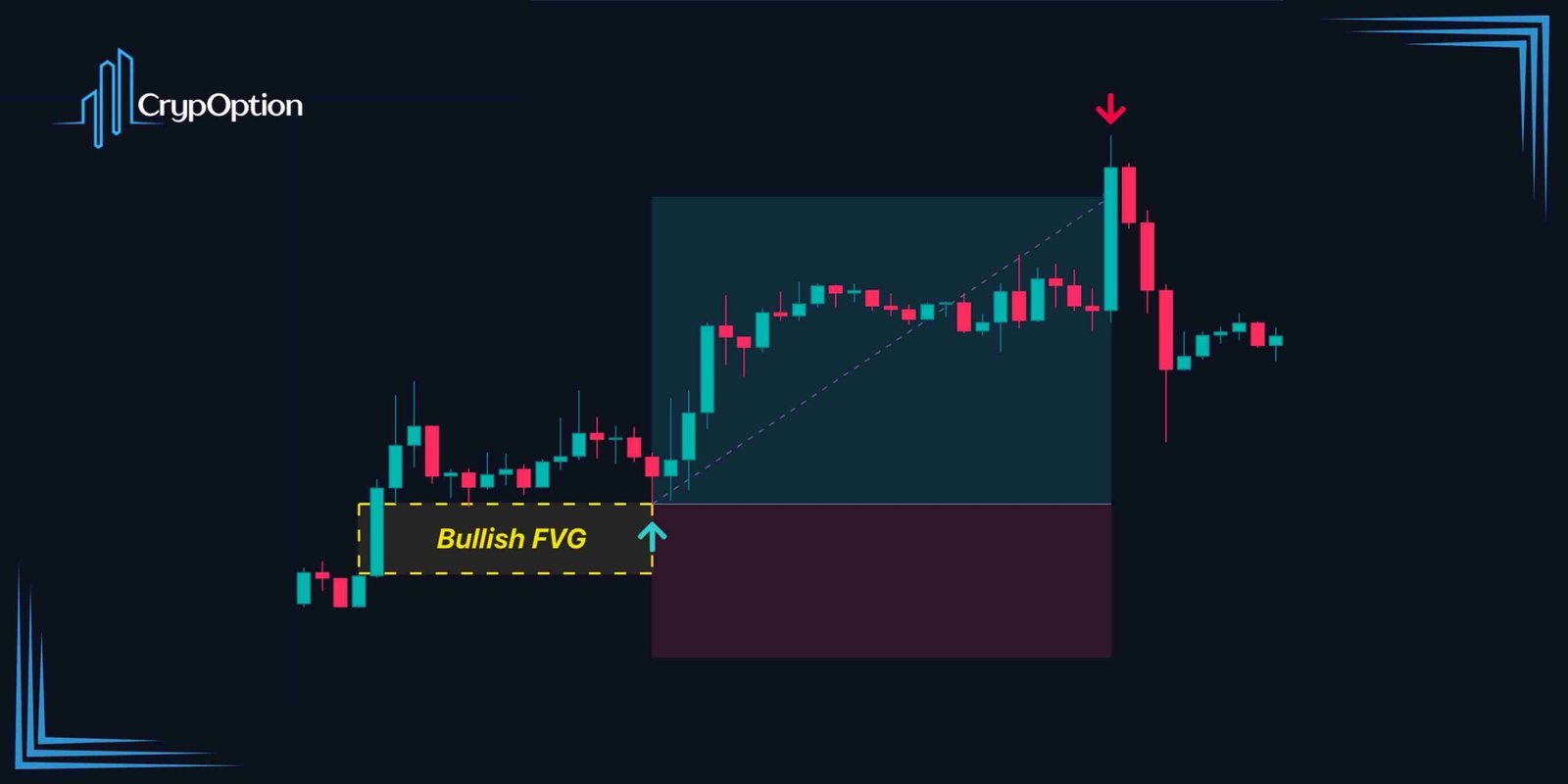
Fair Value Gap Trading Strategy for Binary Options
Binary options trading is all about anticipating the direction of the price in a specified timeframe. While many traders use indicators to trade binary options, I’m about to show you how you can use ICT Fair Value Gaps for this cause.
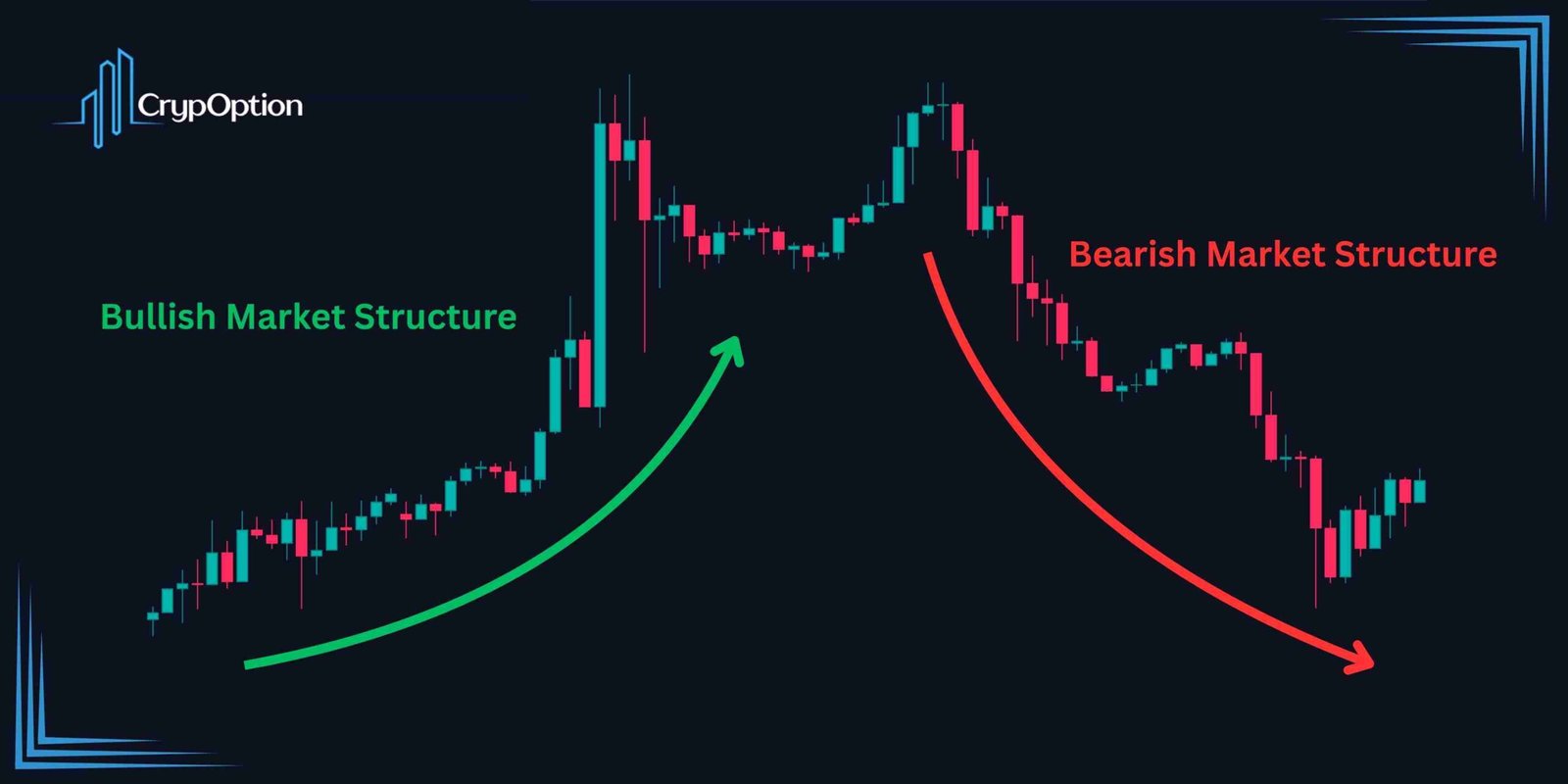
So, let me present my personal FVG binary options strategy. First, you should identify the trend, or as known in ICT concepts, the market structure. As you might’ve already heard, “The trend is your friend.” So, executing positions in the direction of the prevailing market structure significantly boosts your winning probability.
In ICT concepts, we determine the market structure with simple price action methods. If the market is creating higher highs and lows, the market structure is bullish. On the contrary, lower highs and lows show a bearish market structure. Therefore, our first step is to identify the trend using this method. You can use indicators like the Supertrend indicator for easier trend identification.
Next, we should identify a fair value gap that is in the direction of the trend. For example, if the market structure is bullish, we should look for a nearby bullish one. As already explained, FVGs can act as support and resistance elements. They also tend to reject the price quite early if they are valid.
This is perfect for binary options trading. Our strategy will be to execute a binary options trade as soon as the price pulls back and reacts to the FVG. You can then set the expiration time of the option from one to 5 candles later. For instance, if you are trading on the 1-minute timeframe, you set your expiry from 1 to 5 minutes later.
Yet, one of the most important factors when it comes to trading ICT concepts is time. Check out the best times to trade binary options.
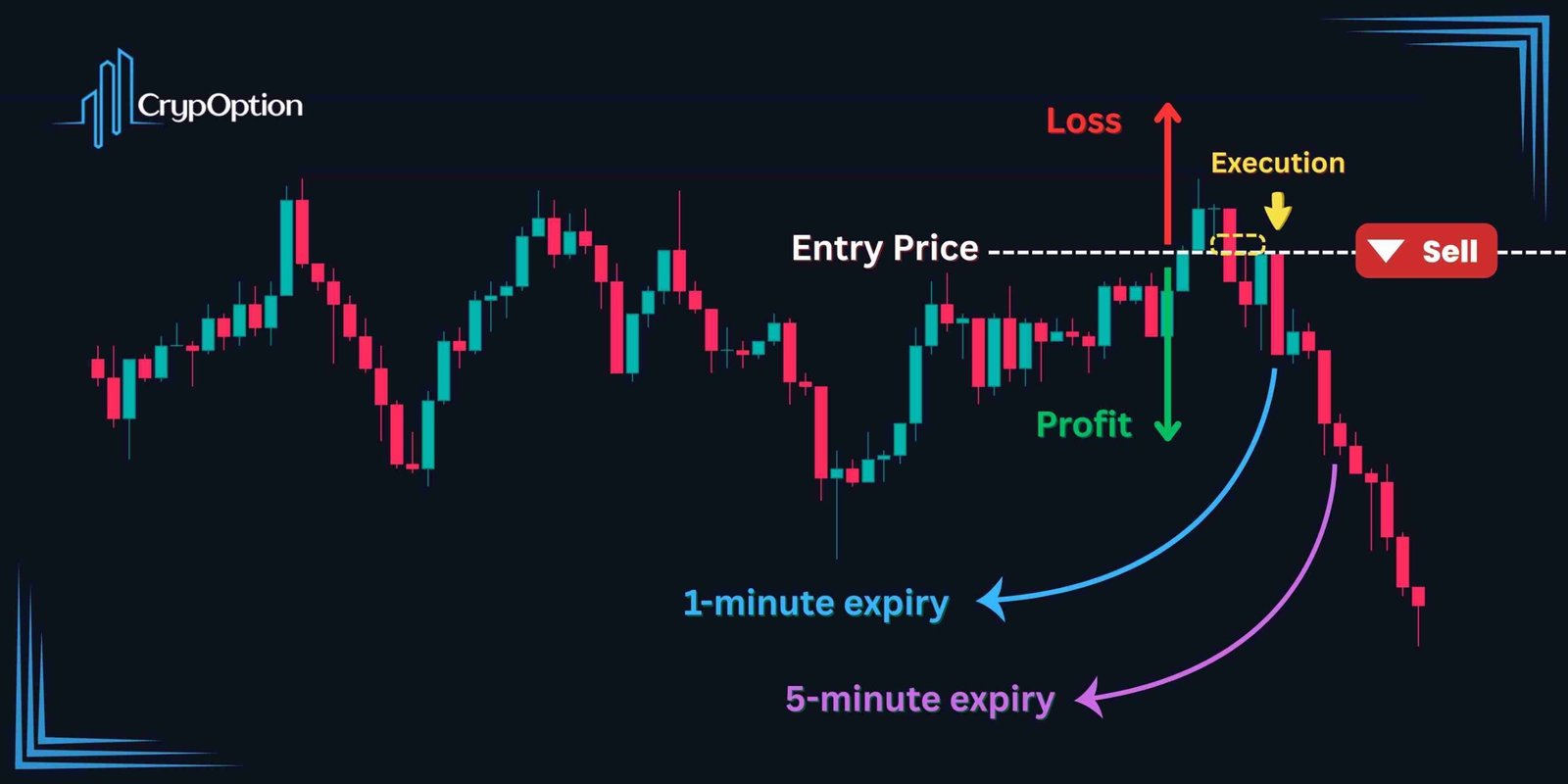
Pro Tip: Trade the Inner Circle Trader’s concepts during the ICT Killzones for the best outcomes.
Common FVG Trading Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Even though fair value gaps are powerful tools, many traders misuse them and almost always blame their failure on the concept. However, low win rates and inconsistent results when trading these patterns are mainly due to our own mistakes or simple statistics, and I have learned this the hard way during my trading career. So, here are the primary pitfalls you should know about and the solutions I’ve personally used to avoid them.
1. Misidentifying Weak FVGs
Not all FVGs are tradable. You should not enter positions based on weak gaps that lack confluence with the overall market narrative. A strong one should be formed by an impulsive move, AKA Displacement, and ideally indicate a move toward a liquidity pool.
Solution: Focus on FVGs that appear after liquidity sweeps, inside a displacement, and cause a break of a recent high or low (Break of Structure).
2. Ignoring Market Structure & Higher Timeframes
Many traders make the mistake of trading every FVG they see, especially scalpers like myself who focus on lower timeframes. This leads to overtrading, frustration, and consistent losses.
Solution: Always check higher timeframes, even if you’re a day trader or scalper (H1, H4, D1), to confirm the trend and make sure the fair value gap aligns with it.
3. Entering Prematurely
Jumping into a trade the moment the price creates an FVG or even taps into one can be risky. Sometimes, the price wicks through the fair value gap before reversing.
Solution: Wait for reaction confirmation, which would be a rejection from the fair value gap that would push the price away in the initial direction.
4. Using Extremely Tight Stop Losses
Placing a stop loss too close to the entry makes it easy to get stopped out by random price fluctuations. FVGs are zones, not precise levels, so the price may slightly extend beyond them before reacting, especially with wicks.
Solution: Give your trade enough breathing room by setting a stop loss below/above recent highs and lows or even below/above the low/high of the previous candle (the one before the FVG candle) rather than inside the fair value gap itself.
5. Ignoring Liquidity Hunts
An FVG is much stronger when the price first sweeps liquidity before creating the gap. If there’s no liquidity grab, most gaps tend to get invalidated and traded through. The same goes for ICT Order Blocks, too.
Solution: Look for liquidity hunts (stop runs) before the price forms an FVG. This increases the probability of your setup.
6. Trading Very Large FVGs (Diminished R/R and Low Probability)
This one is purely from my personal experience: FVGs that are too large require wide stop-losses. This reduces the risk-to-reward ratio. Larger gaps also have a lower probability of working.
Solution: Avoid trading large fair value gaps, especially on lower timeframes. Stick to moderate-sized gaps or even small ones formed in impulsive moves.
Conclusion
ICT concepts are the new trend in the retail trading industry. Many consider them overrated or even fake, but a profitable ICT trader wrote this article for you. The simple concept of fair value gap changed my trading career 3 years ago, and it can do the same for you, too. Of course, you should practice and be disciplined to bring in the profits, like any other trading strategy. Make sure to use demo accounts and backtest your strategies, no matter the concept they’re based on.
I’ve also presented you with a simple yet effective binary options trading method using the ICT fair value gap strategy. Feel free to test and modify this FVG trading strategy as you please. Remember: You will never be profitable if you don’t have a personalized strategy of your own.
For more profitable trading strategies, check out our strategies page.



